When you log onto the system for the first time, you are presented by the System Admin form. Right click on the Company Logo and insert a bitmap (350x190px), pasting in your image. Assuming you entered the correct details during the installation, you can accept all these values without review. You can also add an avatar to your user account if you like:
![]()
Here is the Accounts Mode Home screen (with some outstanding invoices):
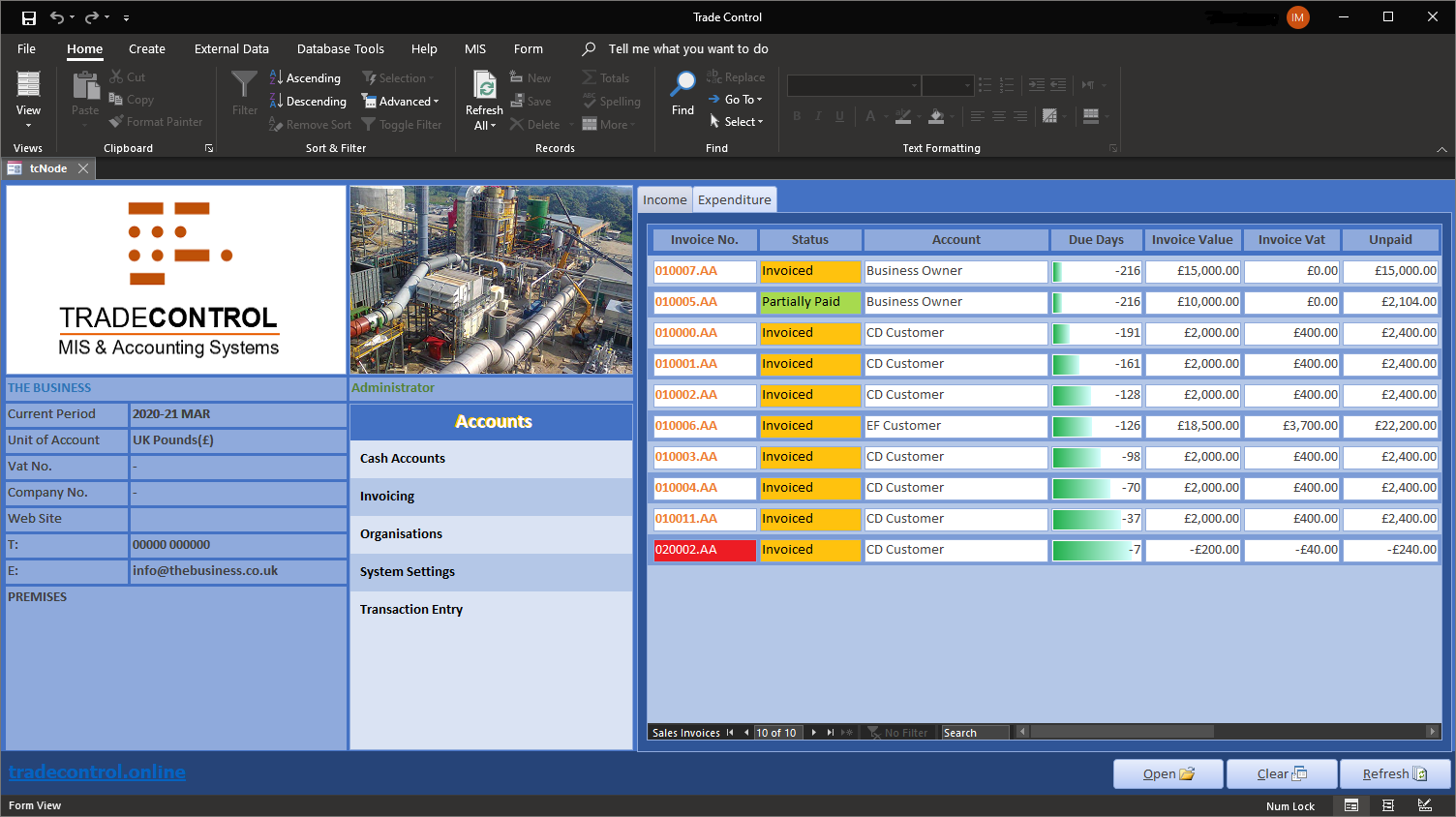
The menu is in the middle section. You will notice that there are not very many options. The reason for that is the way Trade Control models workflows. It classifies transactions by cash polarity rather than by actors and actions, such as customers and suppliers, sales and purchase orders or credit and debit notes. Although not essential, understanding how this works will help you navigate the system effectively:
For the tutorial we are going to start a new company. However, a going concern will need to set the opening balance of its bank accounts. Open Definitions from the toolbar and set the Opening Balance of each bank account at the point of the first transaction.
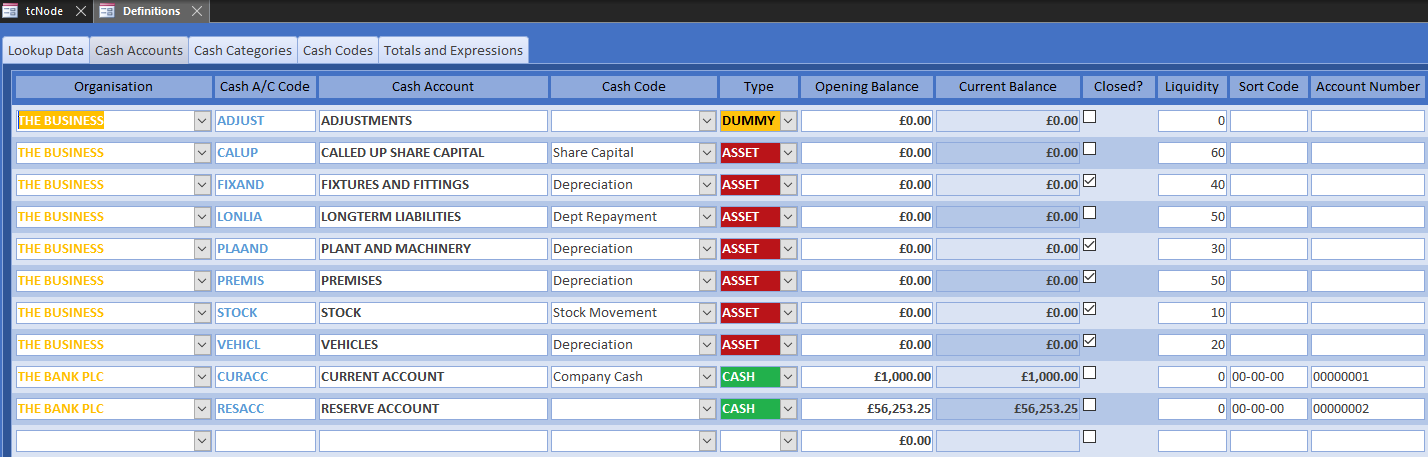
Reference Cash Accounts
If you accept the default cash codes, you can start trading straight away. However, companies that have pre-existing accounts should classify transactions in the same way for historical comparison. In DEBK accounts, nominal codes classify transactions. Trade Control does not have a nominal ledger, but you can translate nominal into cash codes very easily. However, cash codes are structured by categories and therefore it may involve re-configuring them.
Reference Cash Codes
A business needs some money to get going, either by issuing shares or obtaining a loan. For limited copmpanies, it is necessary to inject the share capital at the outset. Most owners issue 1 share each and transfer funds into the business account in the form of a long-term loan.
Pay in the capital injection into your current account by opening Payment Entry. Click New Org in the footer and enter the owner’s name, accept the automatic account code, specify employee, zero payment days and close:
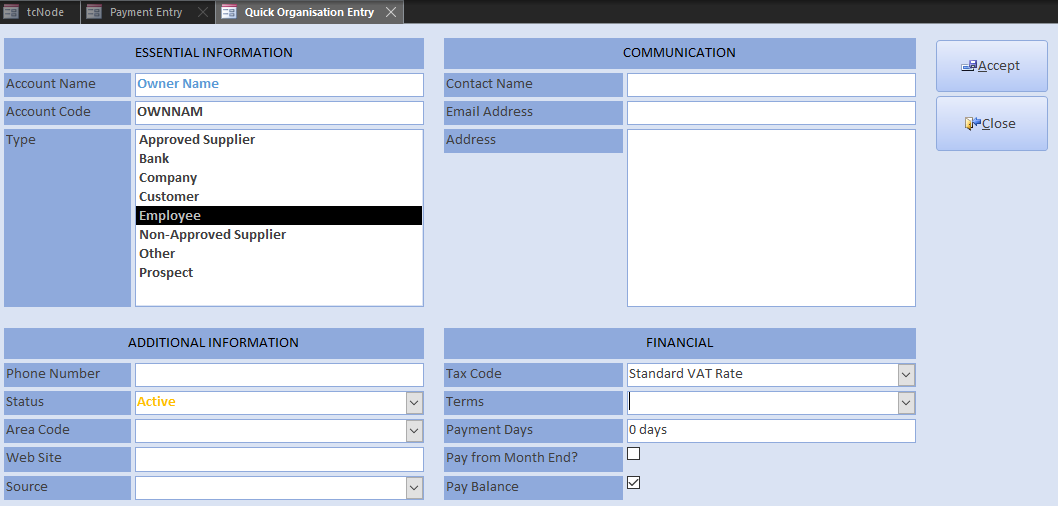
For all transactions, use the 1st of the previous month because the tutorial must post payments retrospectively.
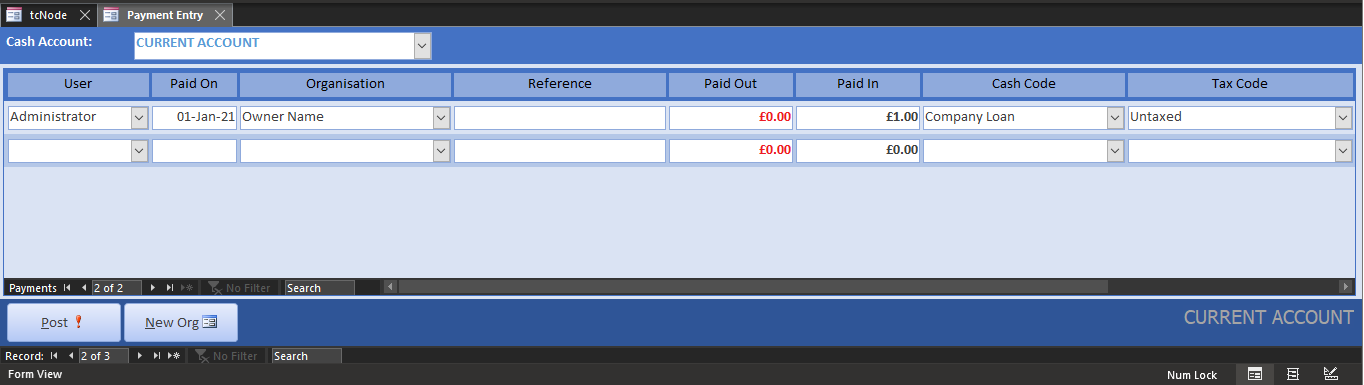
The Share Capital cash code is an asset class which cannot be paid into your bank account. Instead, we pay in the capital as a Company Loan:
Because this is a capital transaction, we must register its effect on the asset value of the business. Open Assets and enter the capital as a liability on the SHARES account:
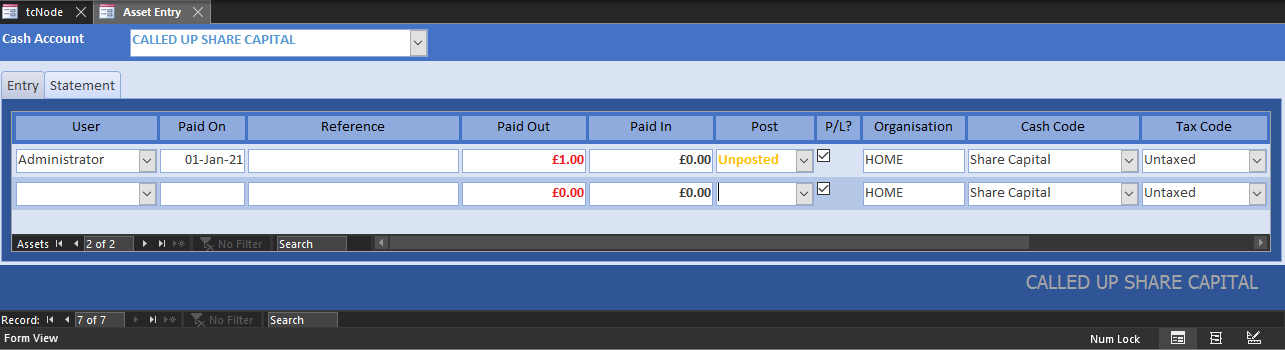
Set the transaction to Posted.
The reason why owners prefer a director’s loan to capital is that they can modify the corporation tax bill at year end by deciding how much to pay back. Because the loan is a long-term liability, it is processed in the same way as we have just completed for share capital. These codes and accounts are installed in the basic setup, so:
Follow the instructions for account transfers and move 5K into the reserve account.
The Cash Account Statement will show a current account of 5,001 with reserves of 5K, a share capital account of -1 and a long-term liability of -10K.
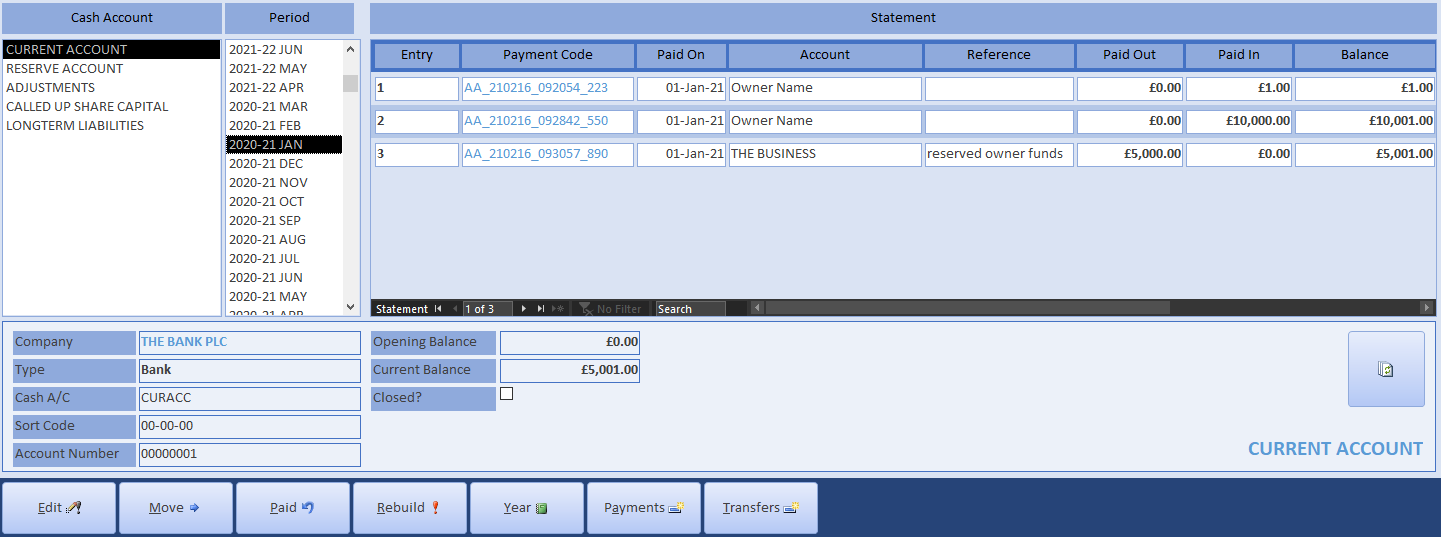
There are two rebuild functions: one for integrating externally imported information or repairing corrupted data; the other for accepting retrospective modifications to a closed period end. Because we are modifying the past, you can accept these changes here since the Cash Statement runs both.
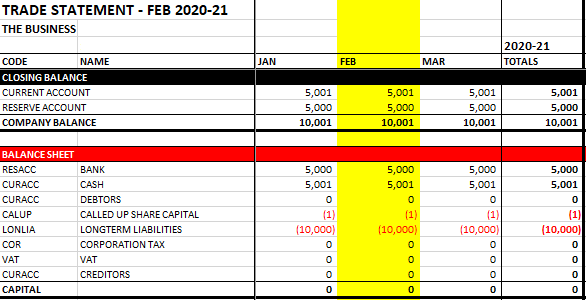
Open the VSTO Excel Trade Statement and run the cash flow. It should look like the following screenshot. Note that the capital value of the business is still zero:
You do not have to invoice in order to use the cash book, you can just make miscellaneous payments which will automatically create invoices for each transaction. However, corporations have a legal obligation to record their asset value rather than current cash position, and invoices are integral to that. Moreover, most companies will want to invoice their customers. If you do not have a separate system for order processing, you can email PDF invoices from the cash book and they will be paid off based on their due dates.
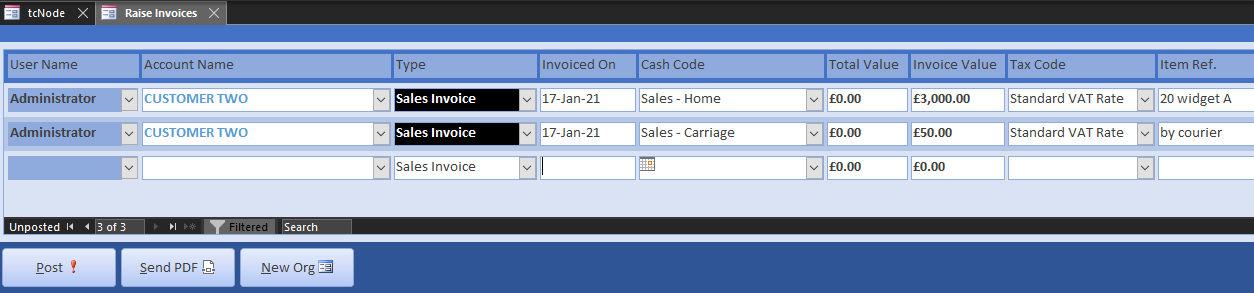
Open Invoicing from the Home menu. Use the New Org button to create new suppliers and customers. When entering customers, specify payment terms and days (such as 30 days or COD), their business and email address. Choose dates from previous months. Here are the entries for a job that assembles and despatches a widget:
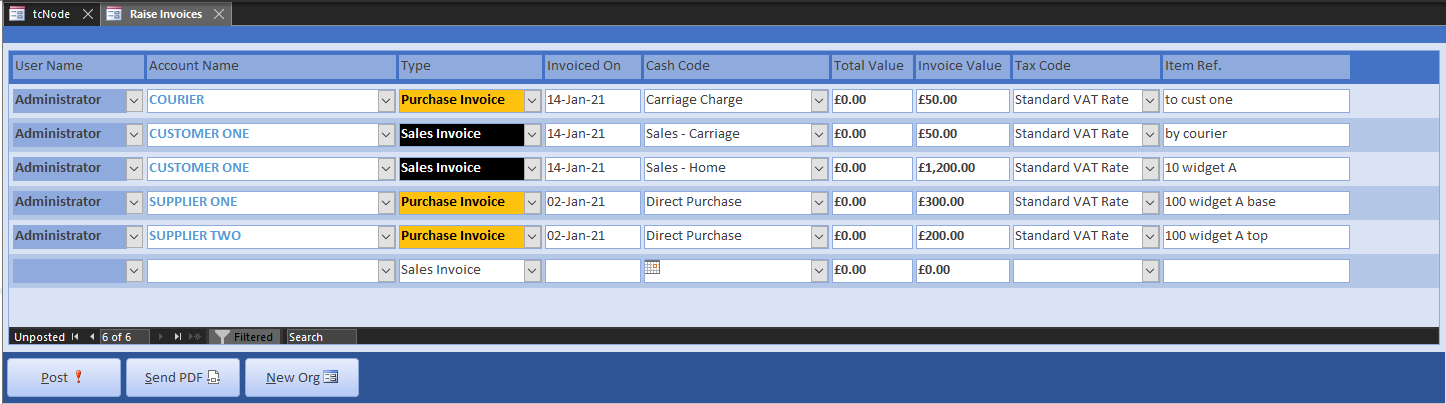
The courier purchase invoice uses a new cash code called Carriage Charges, categorised as a Direct Cost. Post the invoices and select Send PDF to open Invoice Edit filtered by unprinted sales invoices and credit notes.
The Invoice Edit allows you to modify the invoice and add header text. If you did not enter an email and business address when creating the customer, open Organisations and lookup the customer. Enter their email address on the Details page, otherwise you will have to enter it manually. Type their business address into the Addresses page so that it appears on the invoice.
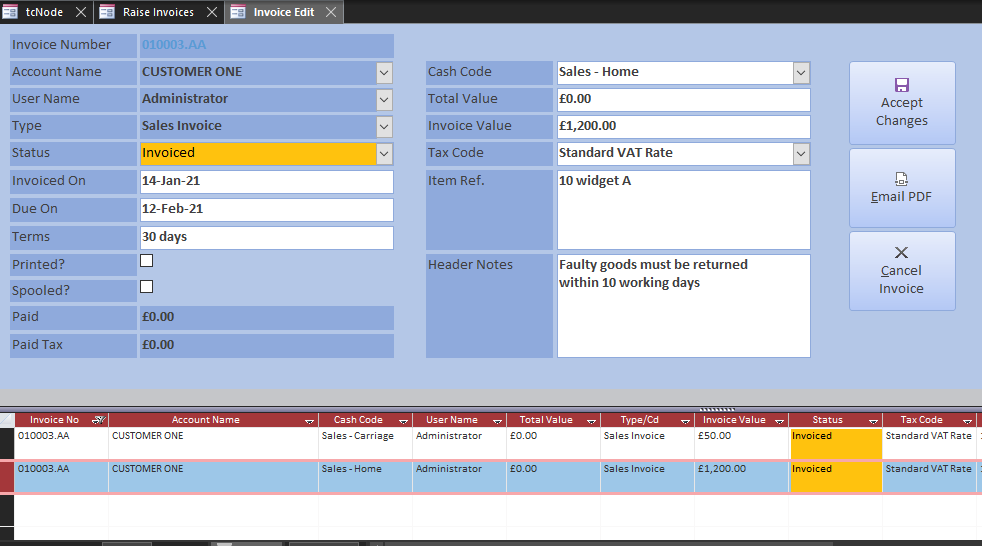
When emailing the PDF, Outlook is instructed to create an email to the default address and attach the selected invoice. You can cancel the email by just closing the Outlook window. The invoice is set to Printed, but you can re-send it at any time.
All external documents can be profiled. Because Trade Control is open source you can do that yourself, or contact us for a quotation.
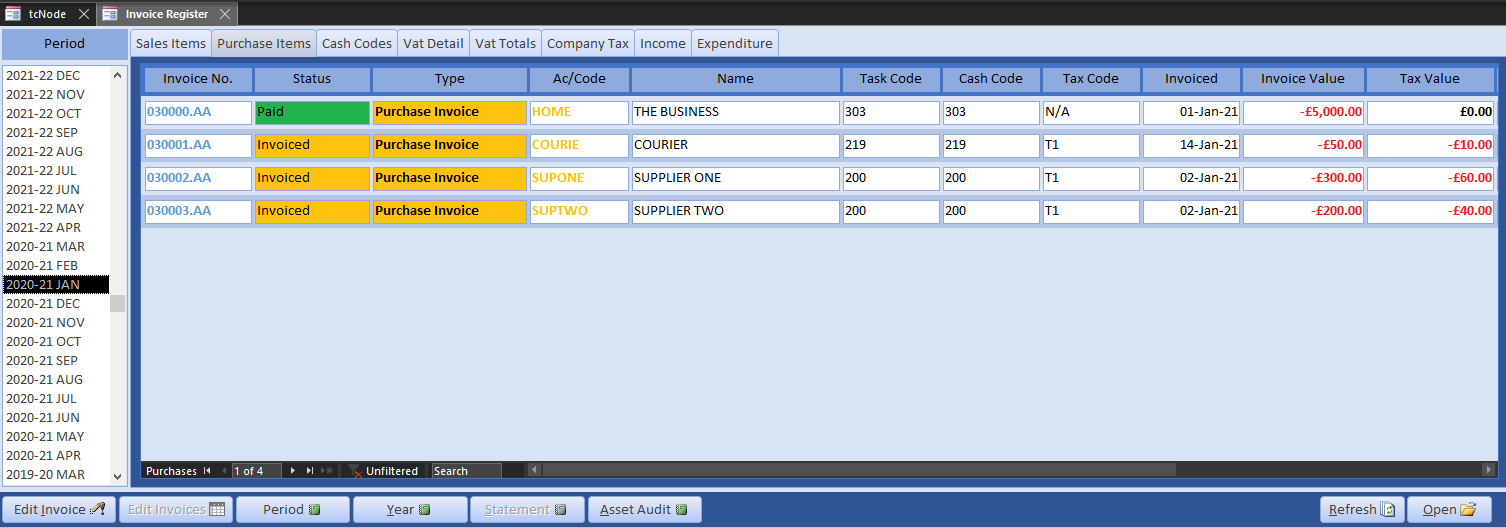
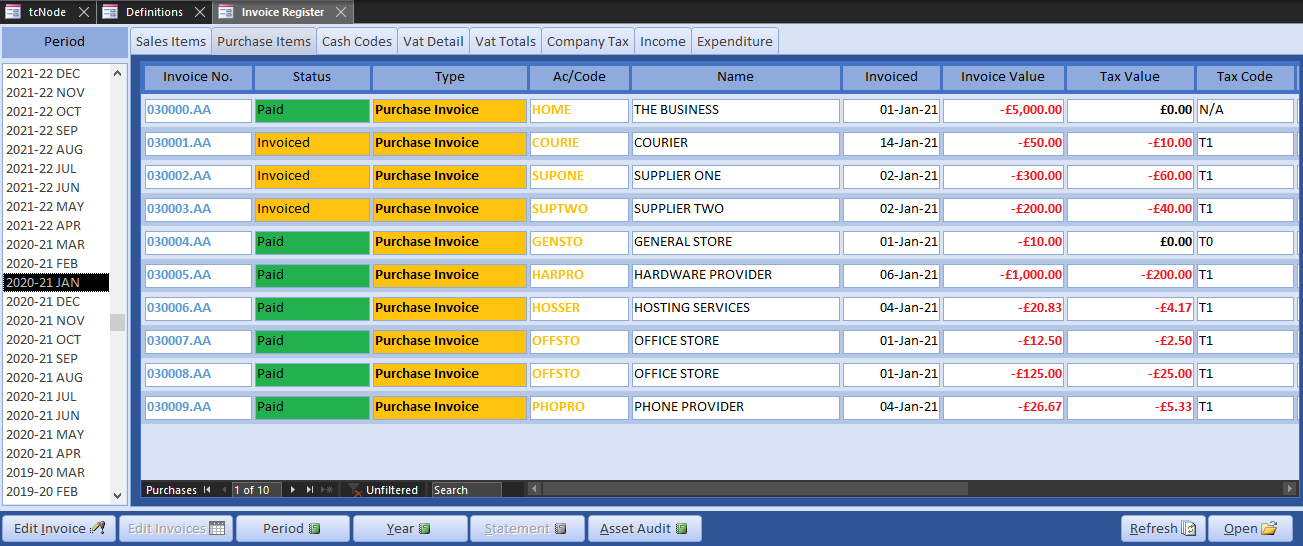
Use the toolbar to clear the workspace and open Invoice Register. We retrospectively entered invoices in the previous month, so select that period. The pages are self-explanatory. Below is a screenshot of the period purchases so far.
And here is our new balance sheet:
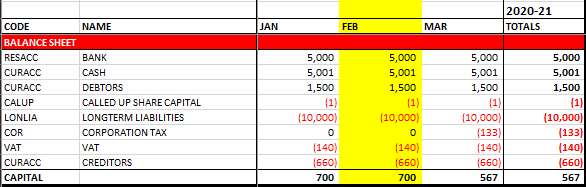
Note how we now have capital, which is the profit on the job. Also, corporation tax is deducted from the capital at year end but will not fall due for payment until the following year.
For the processing of assets and accruals, consult the tutorial on constructing a balance sheet.
This section explains how to mirror your bank account. Perhaps one day this process can be replaced by the Trade Control commercial wallet, which is superior to a bank account in every way. In the meantime, mirroring is still quite straight forward.
It is possible for a sole trader to produce legally compliant books by using miscellaneous payments alone. That is because the SvD algorithm automatically creates invoices, matching a supply for each demand and vice versa. If payments are retrospectively altered, then the SvD balance will be thrown out, resulting in either new creditors or debtors. This is easily repaired by editing the Organisation Statement. Corporations use miscellaneous payment entries for items such as consumables, expenses, salaries, tax and so on.
To make a miscellaneous payment, open Payment Entry and include a cash code in the transaction. That is all. The transactions are entered from your online bank statement. Therefore, once posted the bank balance must equal that on the corresponding cash account. If there is a mismatch, edit the cash account statement.
Here are some purchases our start-up might need, entered in datasheet view with a running total:
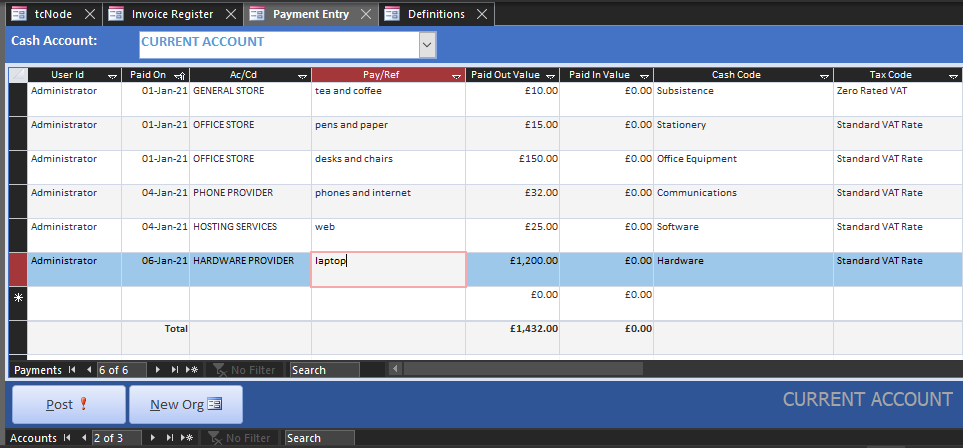
Once posted, open the Invoice Register and there will be paid purchase invoices in the previous period that match these payments (minus vat). You can always move these invoices into different accounting periods. For example, invoices for Employers NI would normally be moved into the financial period to which they apply (although unnecessary if manually invoiced in advance).
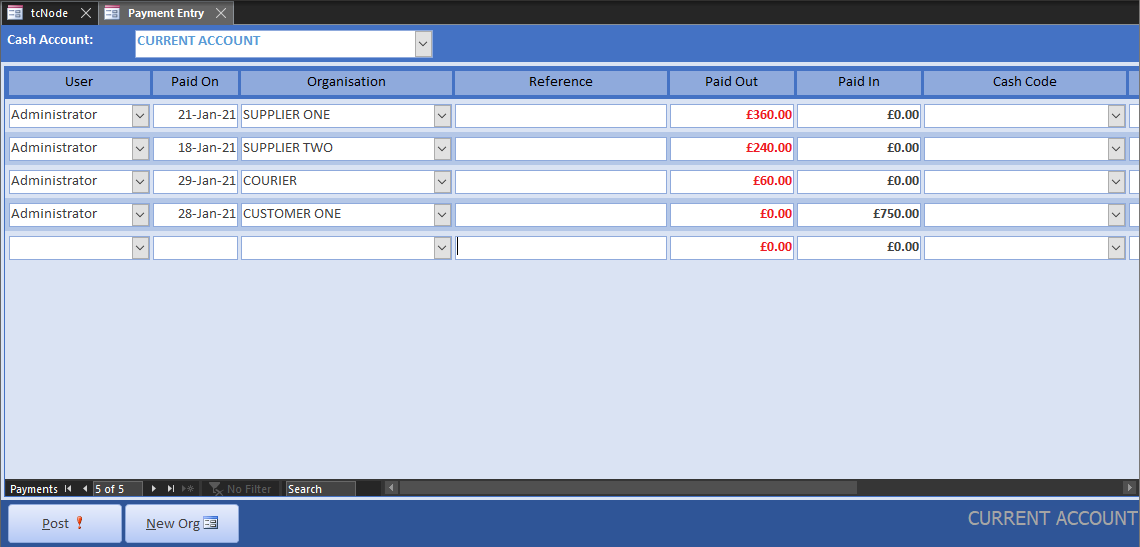
Paying outstanding invoices is the same as making a miscellaneous payment only you omit the cash code. Although this difference seems slight, the algorithm for processing the transaction is very different. Invoices are paid off in date order, so if you want to control the allocation of the money supply to specific invoices, that is the only way you can influence it. Furthermore, you can buy and sell from and to the same account, complicating the allocation process. Whatever the scenario, the algorithm will work out the outstanding balance on the account, thus determining your debtors and creditors. When payment is incomplete, invoices are set to partially paid.
For the tutorial, we pay off all the suppliers, but the customer partially pays their invoice on account. We therefore accept the default paid value for the suppliers and reduce the customer payment to half.
From the Invoice Register, the Sales Items page shows the partially paid invoice. The Organisation Statement for the customer shows a negative balance for the outstanding amount.
The P&L and Balance Sheet now show that the business is in a loss-making position, pays no tax and can reclaim vat on purchases. The profit on then P&L is the same as the capital because capital is initially zero in the first year of trading and there is no corporation tax liability.
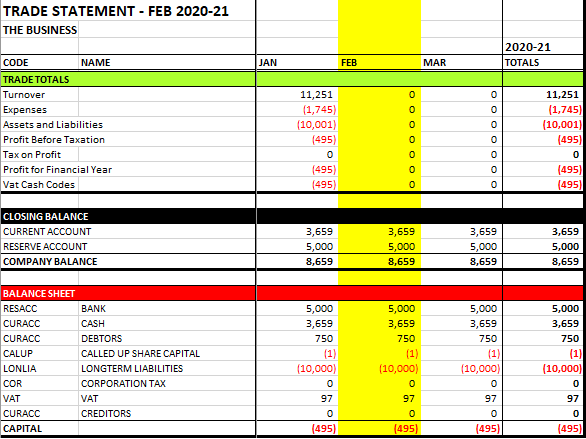
To make some profit, raise an invoice for another customer, then regenerate the Trade Statement to see the effect on profit and capital:
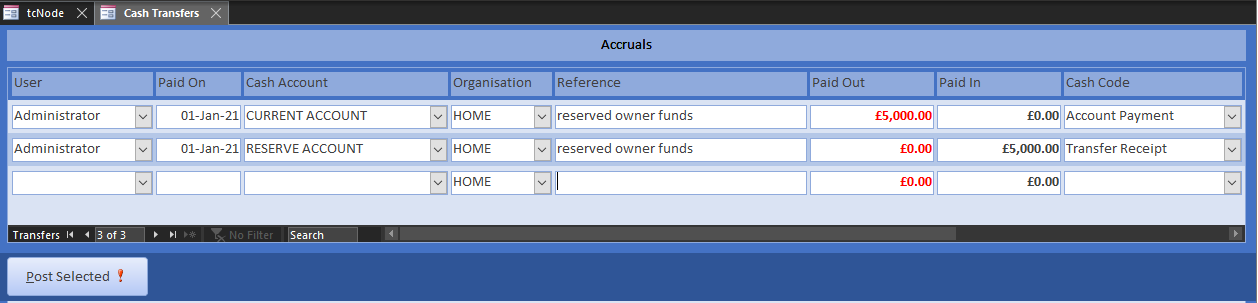
Traditionally, businesses have held a high interest reserve account where savings and tax accruals are deposited. Whilst interest rates are now low, it is still general practice. Open Transfers from the Home menu and move the exact sum between accounts using the relevant cash code.
When trades do not work out there is an application for credit. You apply for credit from a supplier on a debit note, or issue credit to customers on a credit note. For example, Customer One returns a faulty widget and asks for credit. We email a credit note using the same procedure for a sales invoice, only we specify a credit note.
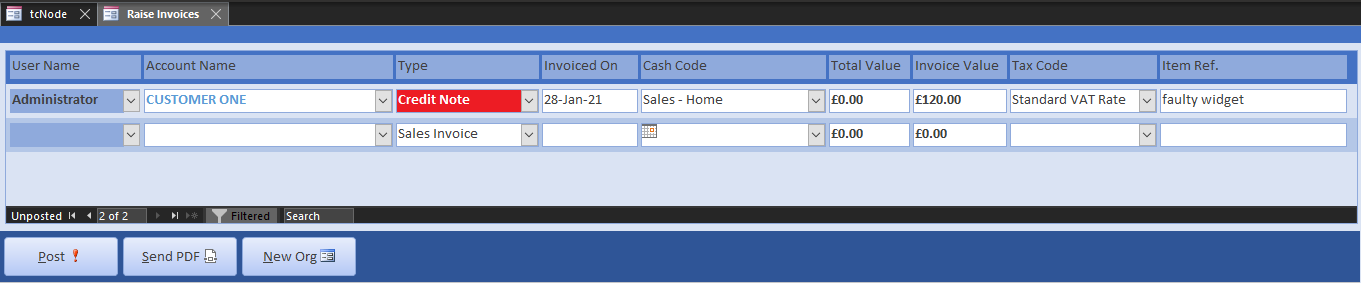
The credit note document is the same as that for debit applications. Often, the latter is not sent out, but credit notes from a supplier will need to be entered as a debit to correct their SvD statement.
accounts_sample_credit_note.pdf
Because we have been changing the past retrospectively, it is necessary to re-build the period end. Open System Admin and click Reset Periods. This re-runs the period-end closedown procedure for historical data, so it can be executed at any time. The only reason for using it is when retrospectively changing the invoice register.
The period end dates below were created during the setup procedure. Looking forward, you need to closedown each month once everything is in order. The period start on dates would only be modified if you were implementing a stock take. To enter new financial years, just the year is required. Press the Reset Periods and it will generate the months automatically. As the years roll by, setting a financial year to archived will remove the associated months from the Cash Statements, Invoice Register and Trade Statements. It will not alter any of the projected SvD balances or tax calculations.
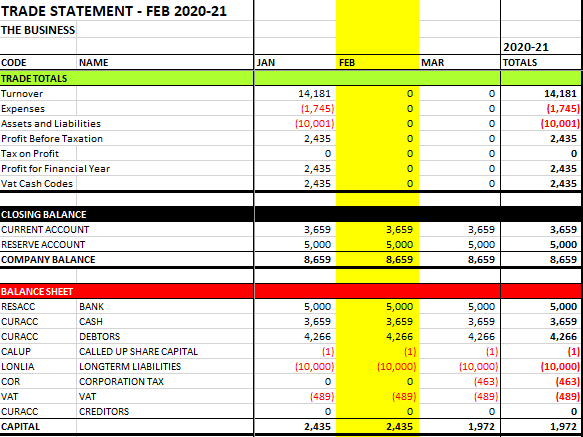
Once all these steps have been completed, you will have generated a legally compliant P&L with an associated Balance Sheet. If you replicated the figures above, the start-up now has 1972 GBP capital, having made 2435 GBP profit in its first month of trading, incurring 463 GBP tax. The Trade Statement should look like this:
From the Home menu, open the Balance Sheet Audit, which will present a list of debtors and creditors by month:

Follow the tutorial on filing your accounts with HMRC for a step-by-step guide on submitting your annual tax return.
The following sections provide informational and technical guidance for generating your company accounts.If you have read the tutorial on cash polarity, you will already know that there are no customers or suppliers in Trade Control, but you can add them. Open Definitions from the toolbar and the page on Lookup Data allows you to create your own classifications. The organisation types below were created during the basic setup routine. These types and their associated polarity are more important when you upgrade to the multi-user MIS, since employees will want to view only the organisations for which they are responsible.
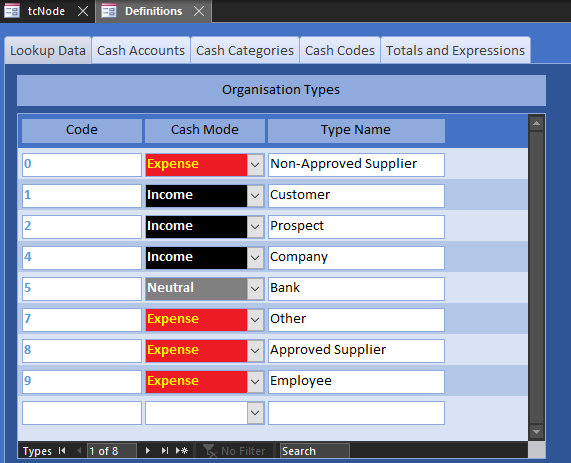
The Organisation Maintenance interface is borrowed from the MIS and therefore has many more options than you will need for producing your books. The key information is as follows:
Optionally, you can store any kind document against an organisation. However, care should be taken if there are restrictions on database size.
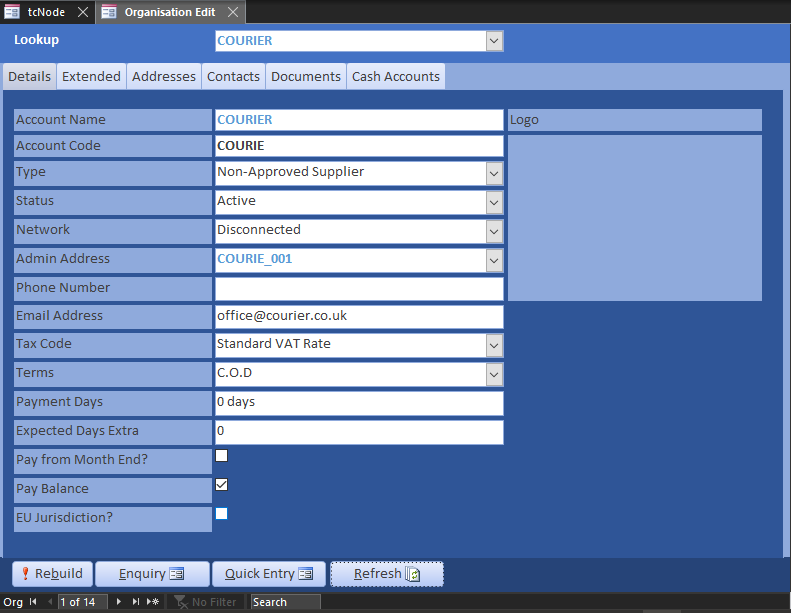
You will likely use the Organisation Enquiry frequently. It is presented in spit datasheet view, but you can open Organisations and select the account from a drop-down list, then open the Enquiry from there. It presents their details, invoices, payments and SvD statement.
For Customer One the statement shows the projected balance. Each month end balance will be the same as that on the Balance Sheet Audit and is used for constructing the debtors and creditors on the balance sheet itself.
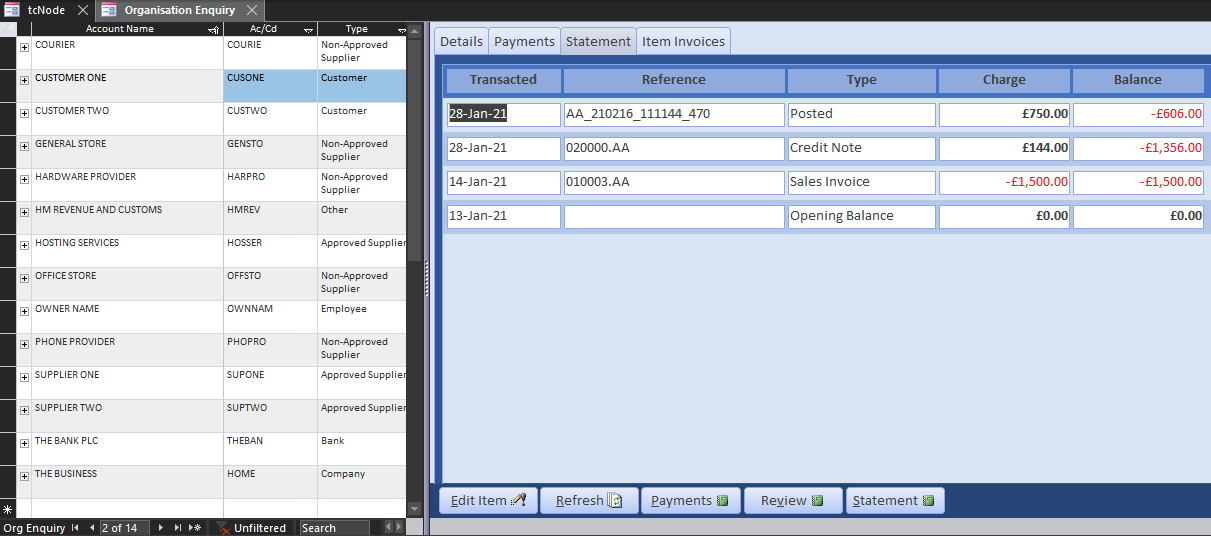
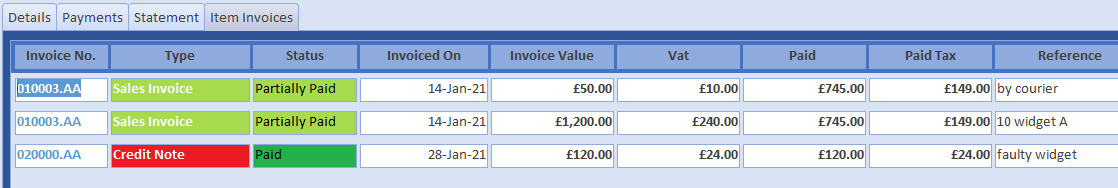
The current balance of the debtor or creditor is also used to set the payment status of the allocated invoices. In live circumstances, the SvD projection can be quite complicated, particularly if both income and expenditure are included on the same account (such as HMRC); but the principle is the same. From the Item Invoice enquiry for Customer One, you can see how the SvD algorithm has calculated the invoice and vat value paid and set the payment status 0f 010003.AA to partial:
The Trade Statement communicates Cash Performance, Profit and Loss and a Balance Sheet. It is also used by the MIS for forward planning and accruals that do not apply in Accounts Mode. For reviewing your accounts, the settings in the XLS Action Pane should be the same as that used for generating a balance sheet.
From the Home menu, the Budget option allows you to set targets for the year.
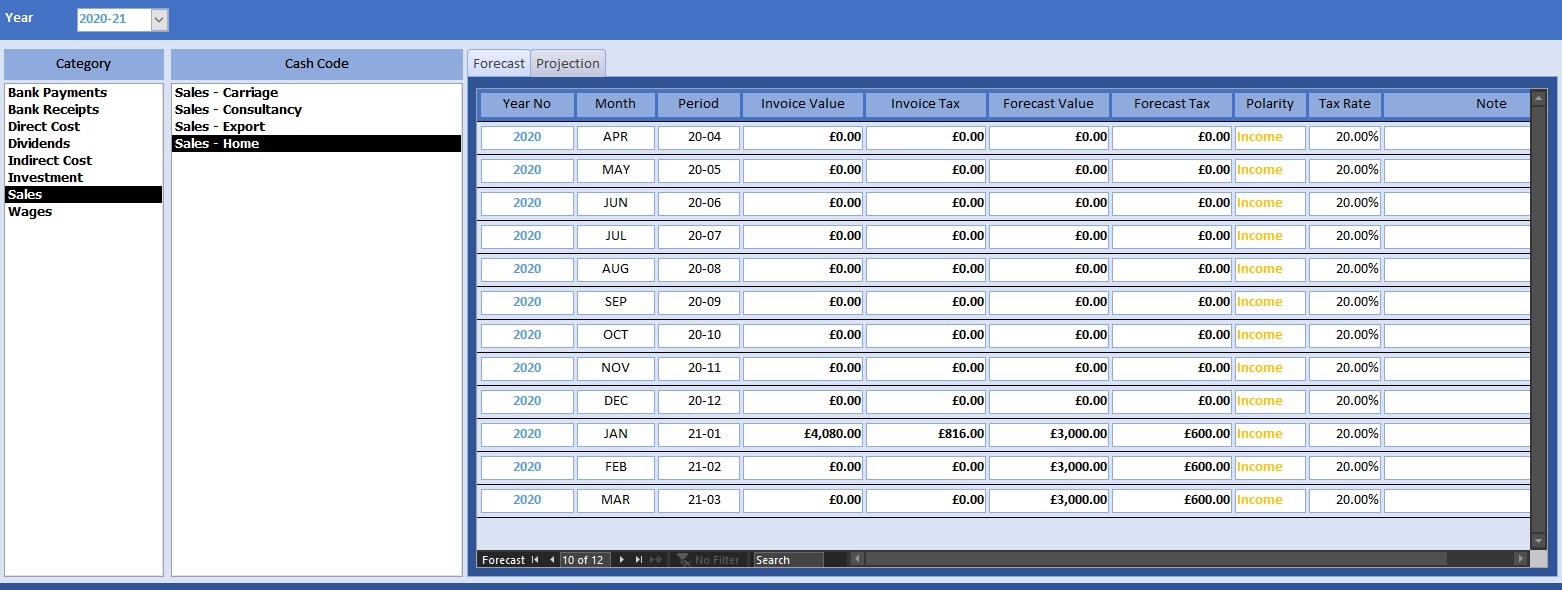
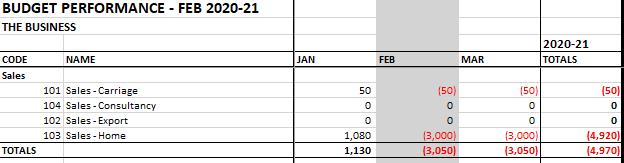
Run the budget using the action pane. We are planning to turnover 3K GBP per month. In our first month of trading, we exceeded that target by 1080 GBP.
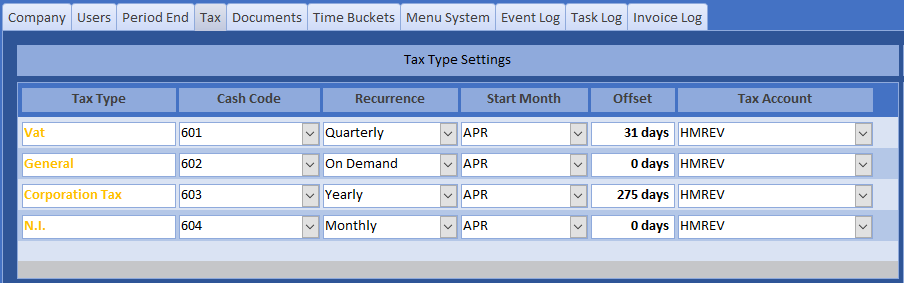
Once you have established the correct settings, they will remain fixed unless there is some structural change to the business. The offset days is used to distinguish tax liability from payment due date. VAT is 1 month, and corporation tax is 9 months. The Tax Horizon is used as a threshold for calculating projected tax on the order book. Since Accounts Mode does not maintain an order book, this setting is not used. The cash codes assigned to control tax types must be assigned to an EXTERNAL Category. The default settings below were configured during the setup process.
Governments change tax rates to stimulate the economy or raise money for social benefit. To deal with this, check out the government portal at the end of each financial year for the latest rates and enter them in the Tax page of the System Administrator. When VAT rates change, you must enter a new code rather than modify an existing one. Trade Control calculates tax statements from the genesis transaction and therefore altering rates will throw out your tax liability.
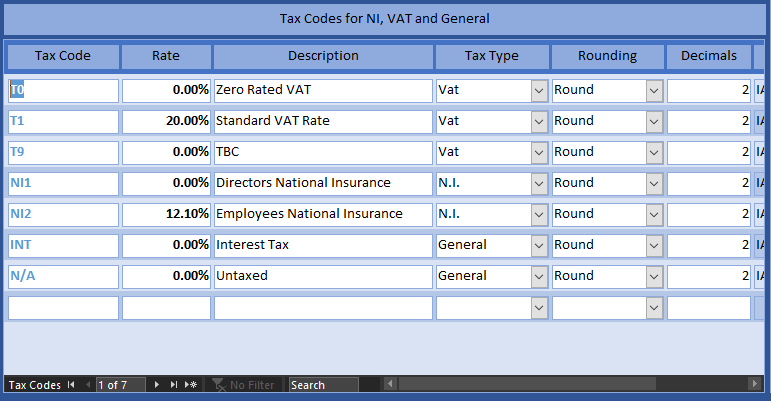
Corporation tax rates are entered by month. You can tweak the tax statements by adjustments. TThis is useful when you first start using the system as a going concern.
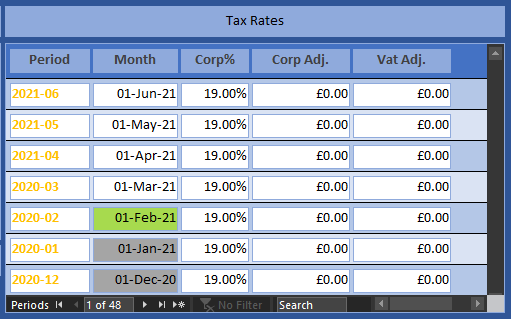
There are two tax statements, for vat and corporation tax. Both are calculated from the genesis transaction in real time using cash polarity and SvD. They are presented in the Invoice Register along with detail pages of the active period. The Vat Statement for the tutorial shows 489 GBP outstanding. Using Payment Entry, pay and post HMRC their dues using the cash code assigned to VAT in tax settings. Press F5 to refresh the Vat Statement, which will now show an outstanding balance of zero. Notice how the payment dates are offset from the balance sheet liability. If you refresh the Trade Statement, VAT will be taken from the balance sheet in January, but the capital will be the same because of the payment.
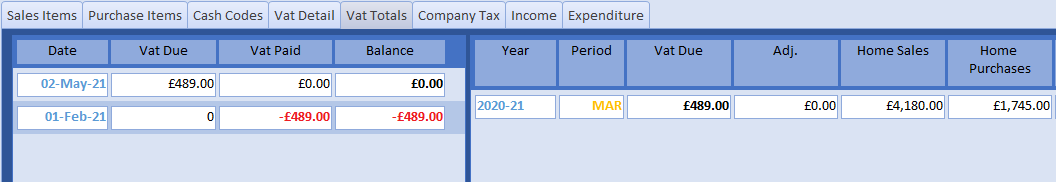
A Cash Account is a set of dated paid in/out transactions, each with a corresponding balance. There are three different types:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| CASH | Maps to your current and reserve bank accounts or bitcoin wallet |
| ASSET | Stores an asset and its write down transactions |
| DUMMY | Adjusts SvD by modifying the invoice register |
CASH type accounts are vital to the effective running of any business. ASSET types do not apply to sole traders, only corporations. The DUMMY type is administrative only, for example, to correct a supplier invoice without a credit note, or vat anomalies.
Because your bank account is mirrored by a cash account, the statement is a useful reference for locating historical transactions. It also allows you to edit and delete any transaction. Modifying cash payments triggers a discrete re-build on the effected organisation, ensuring invoice status matches the projected SvD balance.
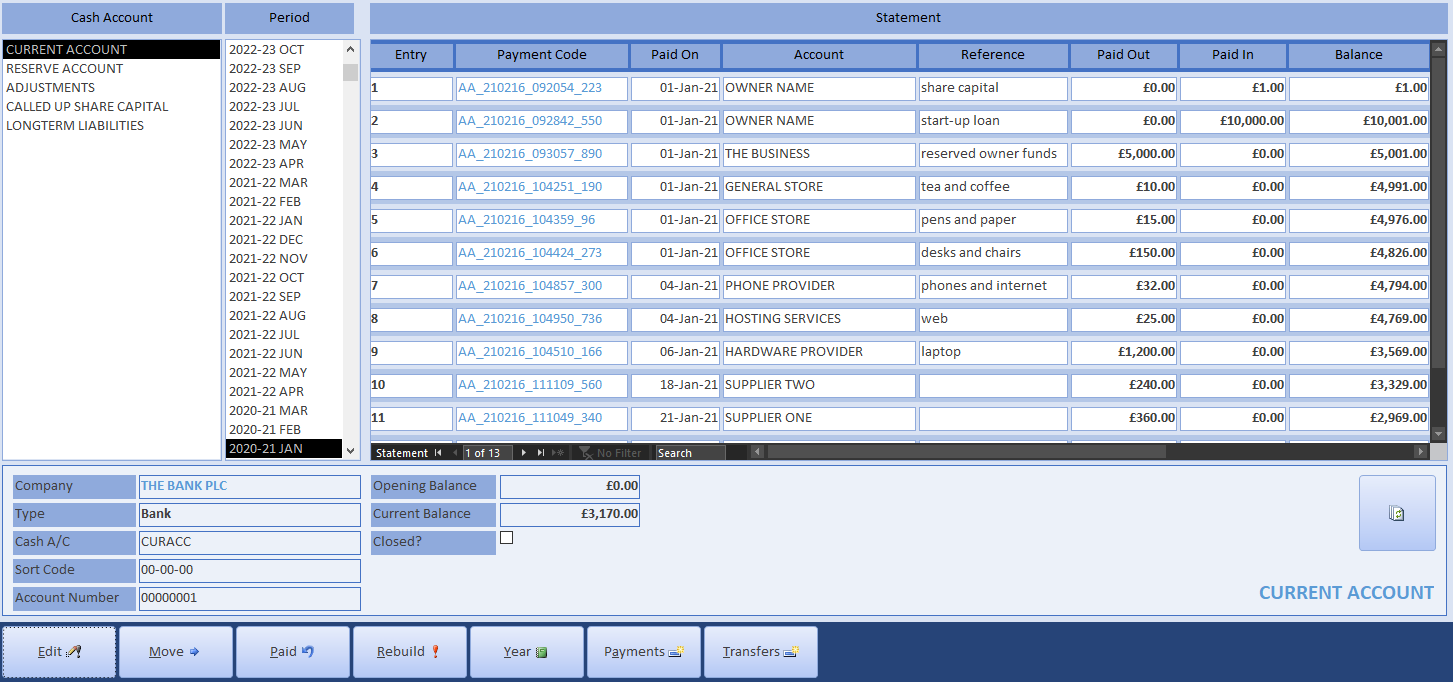
The Rebuild button should only be required if the database has been externally modified or you have retrospectively modified invoices while producing the year-end accounts. It may take a while, but it will not do any harm. The rebuild procedure is also available for specific organisations, which is faster.
Once up and running, you will seldom need to create new cash codes to classify financial transactions. The easiest way is to copy an existing cash code in the same category. There is a tutorial on cash classification for details on how to do this.
During the tutorial, we used the Administrator to review tax and set period end dates. The Accounts Mode can also be used in a multi-user environment by moving the database to Azure Sql or a licensed server. The User page lists employees with system access and specifies status and rights. Multi-user environments are more involved because they involve privileges and permissions. Use the Node Configurator to add new users or upgrade their permissions.
Logs are presented in the Administrator. Any error that occurs on the backend is written to an Event Log, which also includes informational entries. Most errors are likely to be integrity check failures, but more serious failures should be reported to support. The Administrator allows you to clear down the log files if you are running out of space.
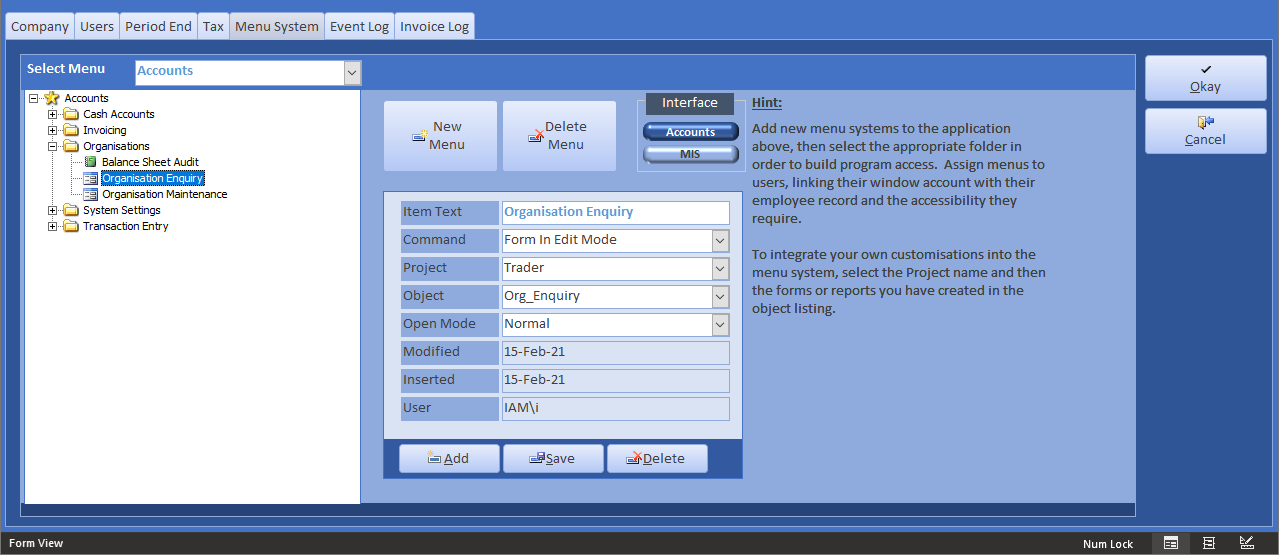
You can create new menus and add your own custom forms and reports if you need to. Contact support for our customisation services.
Incorporated businesses will also need to know how to generate a balance sheet.
Trade Control Documentation by Trade Control Ltd is licenced under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License
